Python dominates North American tech, accounting for 32.43% of programming language interest in the U.S. It surpasses Java (11.71%) and JavaScript (5.46%) due to its simplicity, versatility, and strong presence in AI, machine learning, and data science. In 2024, Python became GitHub's most-used language, with a 49% growth in contributors in 2025. Its role in tools like PyTorch and TensorFlow, combined with educational adoption, ensures a steady influx of new developers. Python's ecosystem also addresses performance challenges with tools like Rust-powered uv and Ruff, making it a top choice for both beginners and professionals. Developers earn competitive salaries, with senior machine learning engineers making $212,928 annually. While JavaScript leads in web development and Java excels in enterprise systems, Python's rise reflects a shift toward data-driven innovation.
1. Python
Adoption in North America
From 2024 to 2025, Python's popularity among developers surged by 7 percentage points, reaching 57.9% [12, 13]. This marks the largest increase seen in the past decade. On GitHub, Python's contributor base grew by 49% year-over-year, propelling it to the top spot [3, 5]. Meanwhile, Jupyter Notebook, a favorite among North American data scientists, saw a remarkable 92% increase in usage during 2024 . The United States continues to dominate globally in GitHub contributions, particularly in generative AI projects .
But beyond these numbers, Python’s real power lies in how it’s being used across industries.
Applications in Key Sectors
Python has become the go-to programming language for artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data science within North American businesses. Major frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow, and Hugging Face Transformers are all built on Python [5, 9]. Among Python developers, 41% are focused on machine learning projects, while 51% are engaged in data exploration and processing tasks [12, 8].
In the U.S., Python developers are well-compensated, with average salaries ranging from $120,000 to $150,000 in 2025. Senior machine learning engineers can earn upwards of $212,928 annually [13, 12]. The job market is also thriving, with an estimated 356,700 Python-related roles opening up each year through 2033 . Industries fueling this demand include finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and tech. Web development, in particular, has seen a revival, with 46% of developers using Python for web projects - a trend largely driven by the growing popularity of FastAPI [8, 13].
Developer Ecosystem
Python's growth is supported by a dynamic and expanding developer community. Currently, 86% of Python developers consider it their primary language, and 50% have less than two years of professional coding experience . This strong presence in education ensures a steady influx of new developers into the North American tech scene.
Guido van Rossum, Python’s creator, highlights that its design, emphasizing clarity and simplicity, has made it a cornerstone of open-source projects, AI advancements, and data science innovation .
Performance improvements are also addressing Python's historical limitations. Python 3.13 offers users upgrading from version 3.10 or earlier a 42% boost in speed and reduces memory usage by 20–30% . Tools powered by Rust, like uv and Ruff, provide package management and linting speeds that are 10–100× faster. Additionally, between 25% and 33% of new native code uploaded to PyPI now uses Rust to enhance performance [8, 12]. For large North American companies, these advancements translate into significant cost savings - up to $5.6 million annually on EC2 expenses by upgrading to the latest Python versions .
2. JavaScript
Adoption in North America
JavaScript is the backbone of web development in North America, playing a dominant role in both front-end and full-stack development. Developers skilled in frameworks like React and Node.js are in high demand, highlighting the language’s importance in creating dynamic web interfaces and server-side applications . While Python excels in data science, JavaScript remains the go-to choice for building interactive and responsive web environments.
The developer community for JavaScript is vast and highly active. Around 40% of developers on major platforms are considered power users, frequently experimenting with new frameworks and tools as part of their workflow . This constant exploration drives innovation, introducing fresh libraries and methodologies that keep the ecosystem evolving. JavaScript’s widespread use underscores its adaptability across various tech sectors.
Applications in Key Sectors
JavaScript serves as a cornerstone for web development across North America's tech landscape. Front-end developers rely on it to craft user interfaces and enhance user experiences. Node.js developers handle server-side applications and runtime environments, while React developers specialize in building modular, component-based UIs. Full-stack developers bridge the gap, leveraging JavaScript for both client-side and server-side tasks .
Industries like e-commerce, startups, and large enterprises rely on JavaScript to unify their development processes. By using tools like Visual Studio Code, developers streamline workflows from coding to deployment . Businesses also turn to professional platforms to connect with JavaScript developers for projects involving cloud services, developer tools, and product launches . As the tech landscape evolves, JavaScript’s ecosystem continues to adapt, meeting the needs of modern developers.
Developer Ecosystem
JavaScript's ecosystem is deeply rooted in web development, contrasting with Python’s focus on data-centric applications. The community includes a wide range of professionals - front-end, Node.js, React, and full-stack developers - who collectively shape the digital experiences that North American users interact with every day . On platforms like daily.dev, which boasts over 1,000,000 members, JavaScript developers form a significant portion of the user base . This vibrant community thrives on rapid innovation, with new tools and frameworks regularly emerging to tackle evolving challenges.
A notable trend is the shift toward machine-readable documentation, which is transforming how developers interact with new technologies. This change doesn’t compete with Python’s data-driven focus but complements it by enhancing JavaScript’s technical capabilities.
As Nimrod Kramer observed on May 11, 2025, "AI agents are now the first to read your docs and touch your platform - not developers. DevRel must adapt by writing for machines: structured, unambiguous, and pattern-rich" .
This shift highlights how AI is reshaping not only the tools developers use but also the way they discover and integrate new technologies into their workflows.
3. Java
Adoption in North America
Java continues to hold a prominent spot in North America, especially for back-end developers, cloud architects, and system administrators. Companies often rely on professional platforms to find and connect with skilled Java developers in the region .
The Java ecosystem showcases its maturity with roles spanning Java, Scala, and Kotlin development. Interestingly, about 1 in 50 developers globally use specialized platforms to stay updated on Java tools and frameworks . This strong presence underscores Java's importance across a wide range of industries.
Applications in Key Sectors
In North America, Java plays a critical role in back-end systems and cloud architecture. It integrates effortlessly with key tools like Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes, making it indispensable for organizations focused on automation and CI/CD pipelines . While Python leads in data-heavy applications, Java remains a cornerstone for industries such as finance and e-commerce . This thriving ecosystem supports continuous growth and expertise, keeping Java relevant in these sectors.
Developer Ecosystem
Java developers benefit from centralized platforms that foster growth and engagement. Around 40% of these developers are considered power users, actively exploring new tools and methodologies . With support for hyper-native environments, Java professionals can stay aligned with industry trends, build networks, and tailor their expertise to specific regions and specialties .
Industry Applications Comparison
::: @figure 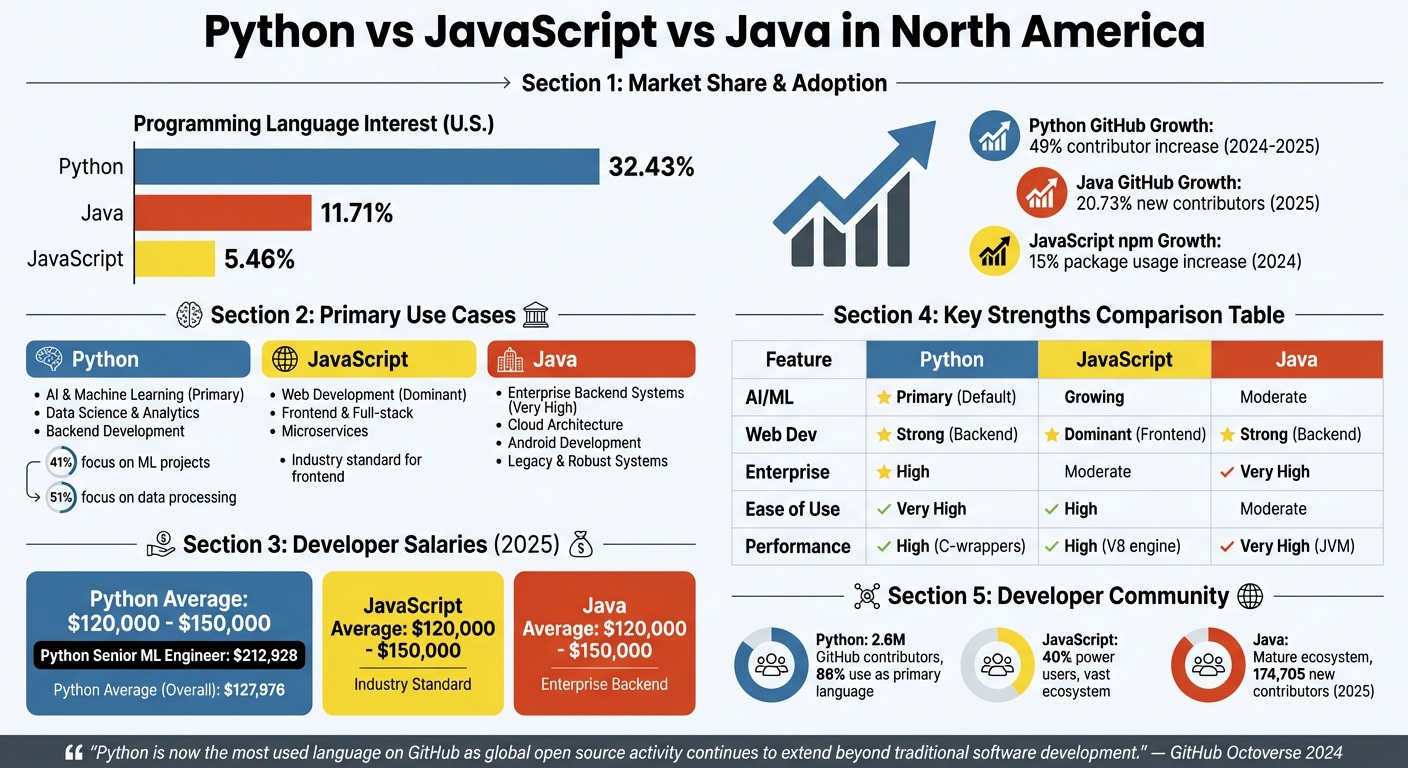 {Python vs JavaScript vs Java: North American Tech Comparison 2025}
{Python vs JavaScript vs Java: North American Tech Comparison 2025}
Each programming language has established a clear niche within North America's tech ecosystem. Python leads the charge in AI and machine learning, becoming the go-to choice for data-driven applications. Its robust ecosystem - featuring tools like NumPy, pandas, and PyTorch - creates a tightly integrated environment, making it challenging for developers to switch to other options . This dominance cements Python's role as a cornerstone of technological innovation in the region.
When it comes to web development, JavaScript reigns supreme, especially for front-end work, where it remains the industry standard. The npm registry reported a 15% increase in package usage in 2024, highlighting the continued growth of its mature ecosystem . On the other hand, Java thrives in enterprise backend systems, offering unmatched stability and scalability. In 2025, Java saw over 174,705 new contributors, marking a 20.73% year-over-year growth, largely driven by its enduring popularity in enterprise development .
These unique strengths across different sectors illustrate how each language meets specific industry demands.
When it comes to performance, each language has its own strengths depending on the use case. Python leverages C-based wrappers to handle computationally heavy tasks efficiently. JavaScript, powered by the V8 engine, excels in asynchronous operations, while Java's JVM and multithreading capabilities shine in large-scale systems. However, ease of use has become a critical factor in language selection. Python's simple and readable syntax allows developers to write less code and focus on solving problems rather than grappling with complex syntax .
"Python is now the most used language on GitHub as global open source activity continues to extend beyond traditional software development."
- GitHub Octoverse 2024 Report
| Feature/Industry | Python | JavaScript | Java |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI/ML Relevance | Primary (Default for research/models) | Growing (Web-based AI/Agents) | Moderate (Enterprise AI integration) |
| Web Development | Strong (Backend/Data-heavy apps) | Dominant (Frontend & Fullstack) | Strong (Large-scale Backend) |
| Enterprise Systems | High (AI/Data integration) | Moderate (Microservices) | Very High (Legacy & Robust Systems) |
| Ease of Use | Very High (Readable, simple syntax) | High (Ubiquitous, flexible) | Moderate (Verbose, strict structure) |
| Performance | High (via C-based wrappers) | High (V8 engine/Asynchronous) | Very High (JVM/Multithreading) |
This breakdown highlights the specific advantages each language offers, setting the stage for a closer look at developer support and community dynamics in the next section.
Developer Support and Community
Python's developer ecosystem in North America stands out when compared to JavaScript and Java. By late 2025, Python had amassed 2.6 million active contributors on GitHub, reflecting an impressive 48% growth over the previous year . This surge aligns closely with the rise of AI development, where Python has cemented itself as the go-to language for many leading machine learning frameworks. Such a thriving community directly contributes to strong regional engagement and educational initiatives.
The numbers highlight Python's regional prominence. The United States alone is home to 14% of the world’s Python developers - the largest share of any single country . This concentration fosters vibrant collaboration and networking opportunities among North American developers, creating a ripple effect that extends into academic and corporate spaces.
In fact, Python has become the backbone of computer science education in North America. Over two-thirds of computer science students in the region now learn Python, bridging the gap between academia and industry . Its "simple but not simplistic" syntax makes it particularly appealing to students and researchers, even those without traditional programming backgrounds . This educational focus ensures that new graduates enter the workforce with a strong grasp of Python, driving its adoption in professional environments.
"Python's clarity and user friendliness compared to Perl was definitely one of the reasons why Python took over Perl in the early aughts." - Guido van Rossum, Creator of Python
Python’s academic popularity has also spurred innovation in tools and frameworks. Modern Rust-powered tools like uv (for package management), Ruff (for linting), and Polars (for dataframes) are addressing Python's historical performance limitations. Today, 33% of binary extensions for Python packages are built using Rust . Additionally, frameworks like FastAPI, an async-first web framework ideal for hosting machine learning models, have seen significant growth, with adoption rising from 29% to 38% recently . These advancements showcase how Python continues to evolve, strengthening its position in both web development and AI applications.
Strengths and Weaknesses
This section dives into the strengths and weaknesses of Python, Java, and JavaScript, particularly in the context of their use across North American tech industries.
Python stands out for its readable syntax and an extensive library ecosystem, with tools like PyTorch and NumPy making it the go-to option for AI and data science applications. In fact, 41% of Python developers use it specifically for machine learning tasks . However, because Python is an interpreted language, it tends to lag behind compiled languages in CPU-intensive operations . These characteristics make Python highly effective for prototyping and research but less ideal for performance-critical applications.
Java, on the other hand, is often the preferred choice for large-scale enterprise systems and Android development. Its strengths lie in performance, stability, and robust multithreading capabilities . Static typing in Java helps catch errors early, which is essential for industries like banking and fintech that demand high reliability. However, Java's verbose syntax can slow down development for smaller projects, as it requires more lines of code compared to Python .
JavaScript dominates in web development and leads in GitHub contributions . Its event-driven, non-blocking architecture makes it indispensable for both frontend and full-stack applications. While not as specialized for AI or enterprise systems, JavaScript’s flexibility and speed for web iterations keep it at the forefront of web technologies.
Here’s a quick comparison of the three languages:
| Feature | Python | Java | JavaScript |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | AI, ML, Data Science, Prototyping | Enterprise systems, Android, Scalability | Web development (Frontend/Backend) |
| Execution Speed | Interpreted (Slower) | Compiled to Bytecode (Faster) | Interpreted/JIT (Fast for web) |
| Typing System | Dynamic (Flexible) | Static (Type-safe, early error detection) | Dynamic (Flexible) |
| Development Speed | Very High (Rapid prototyping) | Moderate (Requires more boilerplate) | High (Fast for web iterations) |
| Concurrency | Limited by GIL for CPU-bound tasks | Robust multithreading support | Event-driven, non-blocking I/O |
| Mobile Support | Very Limited | Strong (Android native) | Moderate (via frameworks) |
Ultimately, the best language depends on specific use cases rather than any inherent superiority. Each one holds a strong position in its respective niche within North America's tech ecosystem, ensuring that developers have the right tools for the job at hand.
Conclusion
Looking at adoption trends, industry use cases, and the strength of its community, Python's dominance in North American tech is undeniable. As of January 2026, it captures over 32% of programming language interest in the United States, far surpassing Java and JavaScript . It even claimed the title of the most popular language on GitHub in 2024, driven by the surge in generative AI projects [3, 11].
Python's growth is nothing short of impressive. By August 2025, its GitHub contributor base had expanded by 48.78% year-over-year, and Jupyter Notebook usage saw a staggering 92% increase in 2024 [3, 9]. With 51% of users focused on data processing and 86% using it as their primary language, Python stands at the forefront of AI and machine learning development .
While JavaScript continues to dominate web development and Java remains a staple for enterprise systems, Python's ecosystem has created a gravitational pull that's hard to rival. Libraries like NumPy, pandas, and PyTorch have established a robust infrastructure that would be incredibly challenging to replace . This technical advantage is mirrored in the job market, where Python developers earn an average of $127,976, and senior machine learning engineers command over $212,928 annually .
Python's influence isn't just about its current dominance - it’s shaping the future. It serves as a gateway for new talent, with 50% of Python developers having less than two years of professional experience . As AI continues to transform the tech landscape in North America, Python remains at the heart of this evolution, driving advancements in AI and data science while laying the groundwork for what’s next.
FAQs
Why is Python more popular than Java and JavaScript in North America?
Python’s widespread use in North America can be attributed to its flexibility and user-friendly design. It’s a go-to language for fields such as AI, data science, and machine learning, thanks to its extensive collection of libraries and frameworks that streamline complex tasks. Its straightforward, readable syntax appeals to beginners while helping seasoned developers work more efficiently.
Beyond its technical strengths, Python consistently scores high in developer surveys and rankings, showcasing its popularity across education, research, and business applications. Its strong presence on platforms like GitHub underscores its significant role in the region’s tech landscape.
Why is Python so popular in AI and machine learning?
Python stands out as a favorite in AI and machine learning, thanks to its rich ecosystem of libraries, frameworks, and tools. With packages like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, pandas, and NumPy, developers have access to pre-built solutions for tasks such as data preprocessing, model training, and deployment. Its straightforward syntax and extensive documentation make it accessible for newcomers while remaining powerful for seasoned developers.
Another key advantage is Python’s ability to integrate effortlessly with scientific computing tools, cloud platforms, and performance-critical components written in C or C++. This adaptability enables developers to create complete workflows - from gathering data to deploying models - without needing to switch programming languages. Backed by a strong community and supported by major tech companies, Python continues to drive advancements in AI and machine learning across the tech landscape in North America.
What recent updates have improved Python's performance?
Python has seen impressive performance improvements with its recent updates. In Python 3.11, execution speeds became up to 2× faster, making a noticeable difference in how quickly programs run. Then came Python 3.13, introducing a no-GIL (Global Interpreter Lock) build, which greatly improved concurrency for multi-threaded applications - something developers had been waiting for. Python 3.14 kept the momentum going with additional speed boosts, and Python 3.15 took things further by delivering a significantly upgraded JIT compiler along with a new profiling package designed for advanced performance tracking.
These advancements have made Python faster and more powerful, reinforcing its position as a go-to programming language for developers across North America and beyond.

